Sonography
Sonography, also known as ultrasound imaging or diagnostic medical sonography, is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of the inside of the body. It is a non-invasive and safe imaging modality that is widely used for diagnostic purposes. Here are key aspects of sonography:
How Sonography Works:
- Sound Waves:
- Ultrasound machines emit high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) into the body.
- Reflection of Sound Waves:
- These sound waves travel through the body and bounce back when they encounter different tissues and structures. The returning echoes are detected by the ultrasound transducer.
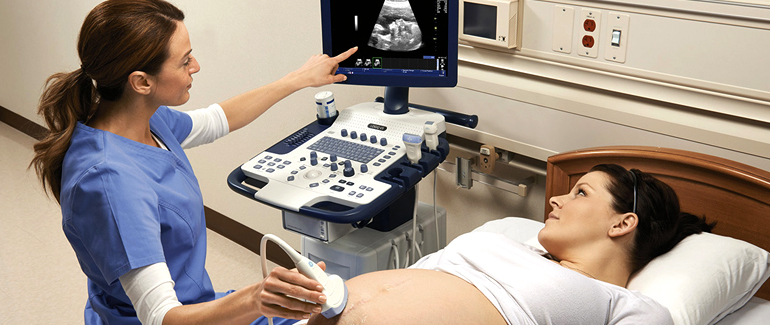
- Transducer:
- The transducer is a handheld device that both emits the sound waves and receives the echoes. It is moved over the skin to capture images of the internal structures.
- Image Formation:
- The echoes are processed by a computer to create real-time images on a monitor. The images can show the size, shape, and consistency of organs and tissues.
Applications of Sonography:
- Obstetrics and Gynecology:
- Sonography is commonly used to monitor fetal development during pregnancy (obstetric ultrasound). It can also assess the health of the uterus and ovaries in gynecology.
- Abdominal Imaging:
- Evaluation of abdominal organs, including the liver, gallbladder, kidneys, pancreas, and spleen.
- Cardiac Sonography:
- Echocardiography uses ultrasound to create images of the heart’s structure and function.
- Vascular Imaging:
- Doppler ultrasound assesses blood flow through veins and arteries, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions such as deep vein thrombosis or carotid artery disease.
- Musculoskeletal Imaging:
- Sonography can visualize muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints, assisting in the diagnosis of musculoskeletal conditions.
- Breast Imaging:
- Breast ultrasound is used as a complementary imaging tool to mammography for evaluating breast abnormalities.
- Thyroid and Neck Imaging:
- Sonography helps assess the thyroid gland and neck structures for conditions such as thyroid nodules or enlarged lymph nodes.
- Pediatric Imaging:
- Sonography is used to evaluate various conditions in children, including abdominal, cardiac, and musculoskeletal issues.
- Urological Imaging:
- Assessment of the kidneys, bladder, and male reproductive organs, helping diagnose conditions such as kidney stones and prostate abnormalities.
Advantages of Sonography:
- Non-Invasive:
- Unlike some imaging techniques, sonography does not involve radiation and is considered safe for patients.
- Real-Time Imaging:
- Sonography provides real-time images, making it useful for dynamic processes such as blood flow or fetal movement.
- Portability:
- Ultrasound machines are often portable, allowing for imaging at the bedside or in various clinical settings.
- Cost-Effective:
- Sonography is generally more cost-effective than some other imaging modalities.
- No Known Side Effects:
- There are no known side effects associated with diagnostic ultrasound when used appropriately.
Sonography is a versatile and valuable tool in medical diagnostics, providing valuable information across various medical specialties. Skilled professionals known as sonographers or ultrasound technologists perform and interpret these examinations, working in collaboration with physicians for accurate diagnosis and patient care.



